
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Drug/Regimen
- Efficacy and Safety of Alogliptin-Pioglitazone Combination for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Poorly Controlled with Metformin: A Multicenter, Double-Blind Randomized Trial
- Ji-Yeon Park, Joonyub Lee, Yoon-Hee Choi, Kyung Wan Min, Kyung Ah Han, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Soo Lim, Young-Hyun Kim, Chul Woo Ahn, Kyung Mook Choi, Kun-Ho Yoon, the Practical Evidence of Antidiabetic Combination Therapy in Korea (PEAK) study investigators
- Received August 7, 2023 Accepted November 30, 2023 Published online April 23, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0259 [Epub ahead of print]
- 184 View
- 8 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
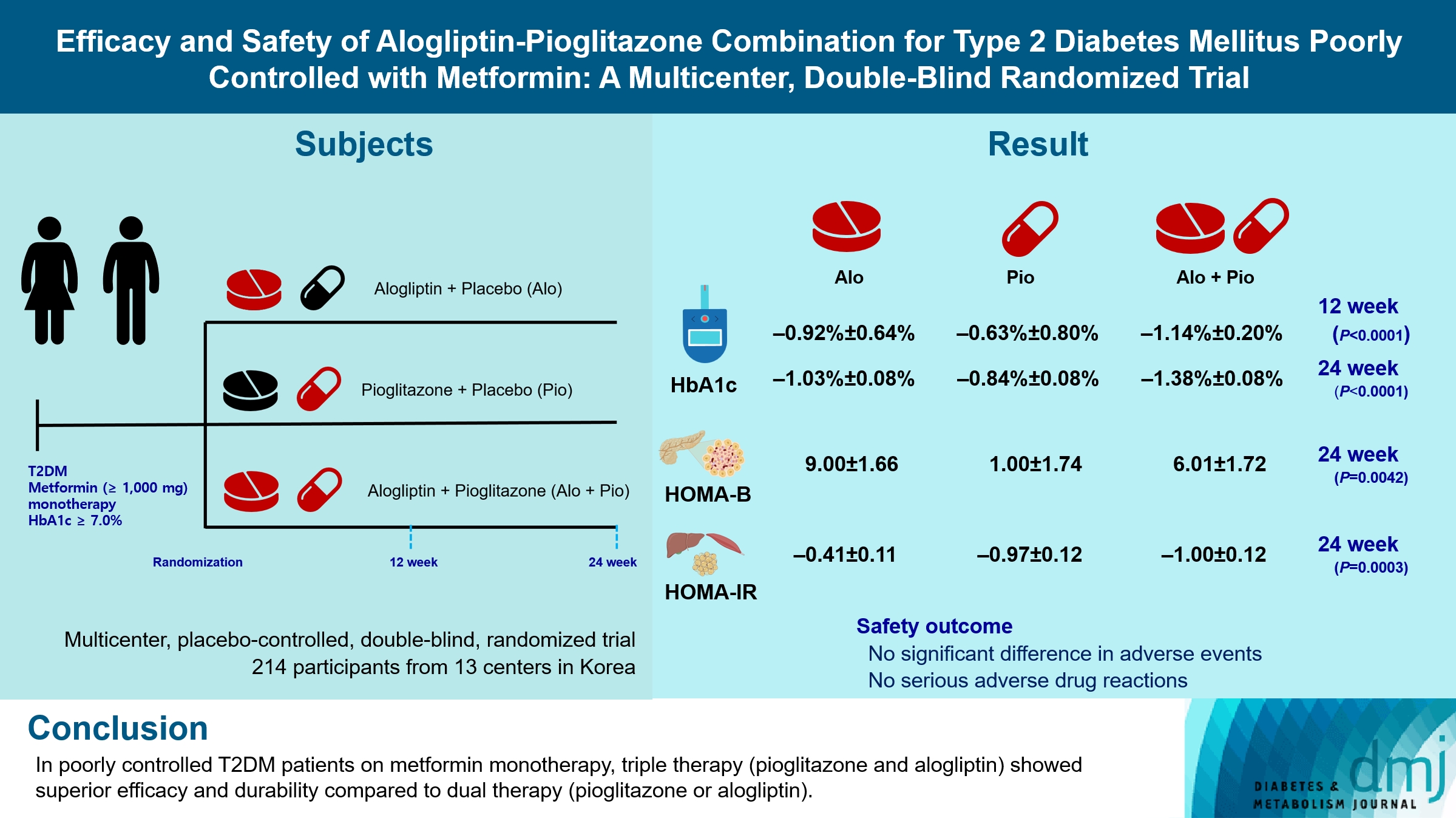
Guidelines for switching to triple combination therapy directly after monotherapy failure are limited. This study investigated the efficacy, long-term sustainability, and safety of either mono or dual add-on therapy using alogliptin and pioglitazone for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) who did not achieve their target glycemic range with metformin monotherapy.
Methods
The Practical Evidence of Antidiabetic Combination Therapy in Korea (PEAK) was a multicenter, placebo-controlled, double-blind, randomized trial. A total of 214 participants were randomized to receive alogliptin+pioglitazone (Alo+Pio group, n=70), alogliptin (Alo group, n=75), or pioglitazone (Pio group, n=69). The primary outcome was the difference in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels between the three groups at baseline to 24 weeks. For durability, the achievement of HbA1c levels <7% and <6.5% was compared in each group. The number of adverse events was investigated for safety.
Results
After 24 weeks of treatment, the change of HbA1c in the Alo+Pio, Alo, and Pio groups were –1.38%±0.08%, –1.03%±0.08%, and –0.84%±0.08%, respectively. The Alo+Pio group had significantly lower HbA1c levels than the other groups (P=0.0063, P<0.0001) and had a higher proportion of patients with target HbA1c achievement. In addition, insulin sensitivity and β-cell function, lipid profiles, and other metabolic indicators were also improved. There were no significant safety issues in patients treated with triple combination therapy.
Conclusion
Early combination triple therapy showed better efficacy and durability than the single add-on (dual) therapy. Therefore, combination therapy with metformin, alogliptin, and pioglitazone is a valuable early treatment option for T2DM poorly controlled with metformin monotherapy.
- Islet Studies and Transplantation
- Alginate-Catechol Cross-Linking Interferes with Insulin Secretion Capacity in Isolated Murine Islet Cells
- Yu-Sik Kim, Seung-Woo Cho, Bomin Ko, Jisoo Shin, Chul Woo Ahn
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(2):164-168. Published online March 28, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.42.2.164
- 3,837 View
- 57 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Over the past three decades, human pancreatic islet isolation and transplantation techniques have developed as a routine clinical procedure for selected patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. However, due to the donor shortage and required chronic systemic immunosuppression, the widespread application of islet transplantation is limited. To overcome these limitations, providing a physical barrier to transplanted islet cells with encapsulating biomaterial has emerged as a promising approach to enhance engraftment and promote islet survival post-transplantation. Alginate has been considered to be a reliable biomaterial, as it enhances islet survival and does not hamper hormone secretion. Alginate-catechol (Al-CA) hydrogel was reported to provide high mechanical strength and chemical stability without deformation over a wide range of pH values. In this study, we, demonstrated, for the first time in the literature, that encapsulation of murine pancreatic islet cells with Al-CA hydrogel does not induce cytotoxicity
ex vivo for an extended period; however, it does markedly abate glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Catechol should not be considered as a constituent for alginate gelation for encapsulating islet cells in the application of islet transplantation.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Alginate-Based Smart Materials and Their Application: Recent Advances and Perspectives
Chandan Maity, Nikita Das
Topics in Current Chemistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Alginate: Enhancement Strategies for Advanced Applications
Alejandro Hurtado, Alaa A. A. Aljabali, Vijay Mishra, Murtaza M. Tambuwala, Ángel Serrano-Aroca
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(9): 4486. CrossRef - Alginate Functionalization for the Microencapsulation of Insulin Producing Cells
N. A. Len’shina, A. N. Konev, A. A. Baten’kin, P. S. Bardina, E. I. Cherkasova, A. V. Kashina, E. V. Zagainova, V. E. Zagainov, S. A. Chesnokov
Polymer Science, Series B.2021; 63(6): 640. CrossRef - Strategies to Functionalize the Anionic Biopolymer Na-Alginate without Restricting Its Polyelectrolyte Properties
Luca Szabó, Sandrine Gerber-Lemaire, Christine Wandrey
Polymers.2020; 12(4): 919. CrossRef - Catechol-Functionalized Alginate Nanoparticles as Mucoadhesive Carriers for Intravesical Chemotherapy
Nitjawan Sahatsapan, Tanasait Ngawhirunpat, Theerasak Rojanarata, Praneet Opanasopit, Prasopchai Patrojanasophon
AAPS PharmSciTech.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Alginate-Based Smart Materials and Their Application: Recent Advances and Perspectives
- The Effect of DPP-4 Inhibitors on Metabolic Parameters in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- Eun Yeong Choe, Yongin Cho, Younjeong Choi, Yujung Yun, Hye Jin Wang, Obin Kwon, Byung-Wan Lee, Chul Woo Ahn, Bong Soo Cha, Hyun Chul Lee, Eun Seok Kang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2014;38(3):211-219. Published online June 17, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2014.38.3.211
- 4,658 View
- 69 Download
- 27 Web of Science
- 25 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background We evaluated the effects of two dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, sitagliptin and vildagliptin, on metabolic parameters in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methods A total of 170 type 2 diabetes patients treated with sitagliptin or vildagliptin for more than 24 weeks were selected. The patients were separated into two groups, sitagliptin (100 mg once daily,
n =93) and vildagliptin (50 mg twice daily,n =77). We compared the effect of each DPP-4 inhibitor on metabolic parameters, including the fasting plasma glucose (FPG), postprandial glucose (PPG), glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), and glycated albumin (GA) levels, and lipid parameters at baseline and after 24 weeks of treatment.Results The HbA1c, FPG, and GA levels were similar between the two groups at baseline, but the sitagliptin group displayed a higher PPG level (
P =0.03). After 24 weeks of treatment, all of the glucose-related parameters were significantly decreased in both groups (P =0.001). The levels of total cholesterol and triglycerides were only reduced in the vildagliptin group (P =0.001), although the sitagliptin group received a larger quantity of statins than the vildagliptin group (P =0.002).The mean change in the glucose- and lipid-related parameters after 24 weeks of treatment were not significantly different between the two groups (P =not significant). Neither sitagliptin nor vildagliptin treatment was associated with a reduction in the high sensitive C-reactive protein level (P =0.714).Conclusion Vildagliptin and sitagliptin exert a similar effect on metabolic parameters, but vildagliptin exerts a more potent beneficial effect on lipid parameters.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Insulin Tregopil: An Ultra-Fast Oral Recombinant Human Insulin Analog: Preclinical and Clinical Development in Diabetes Mellitus
Shashank Joshi, Vathsala Jayanth, Subramanian Loganathan, Vasan K. Sambandamurthy, Sandeep N. Athalye
Drugs.2023; 83(13): 1161. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Treatment with Quadruple Oral Hypoglycemic Agents in Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Multi-Center, Retrospective, Observational Study
Jun Sung Moon, Sunghwan Suh, Sang Soo Kim, Heung Yong Jin, Jeong Mi Kim, Min Hee Jang, Kyung Ae Lee, Ju Hyung Lee, Seung Min Chung, Young Sang Lyu, Jin Hwa Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Jung Eun Jang, Tae Nyun Kim, Sung Woo Kim, Eonju Jeon, Nan Hee Cho, Mi-Kyung Ki
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(5): 675. CrossRef - Vasculoprotective Effects of Vildagliptin. Focus on Atherogenesis
Michał Wiciński, Karol Górski, Eryk Wódkiewicz, Maciej Walczak, Magdalena Nowaczewska, Bartosz Malinowski
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(7): 2275. CrossRef - Anti-inflammatory properties of antidiabetic drugs: A “promised land” in the COVID-19 era?
Niki Katsiki, Ele Ferrannini
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2020; 34(12): 107723. CrossRef Effect of Switching from Linagliptin to Teneligliptin Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors in Older Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Eugene Han, Minyoung Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Hye Soon Kim, Byung-wan Lee, Bong-Soo Cha, Eun Seok Kang
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 4113. CrossRef- Combined vildagliptin and memantine treatment downregulates expression of amyloid precursor protein, and total and phosphorylated tau in a rat model of combined Alzheimer’s disease and type 2 diabetes
Samar S. Khalaf, Mohamed M. Hafez, Eman T. Mehanna, Noha M. Mesbah, Dina M. Abo-Elmatty
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology.2019; 392(6): 685. CrossRef - Therapeutic experience of saxagliptin as first add-on after metformin in Indian type 2 diabetes patients: A non-interventional, prospective, observational study (ONTARGET-INDIA)
Sanjay Kalra, Sarita Bajaj, AG Unnikrishnan, ManashP Baruah, Rakesh Sahay, V Hardik, Amit Kumar
Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2019; 23(3): 312. CrossRef - Cardiovascular Outcome Trials of the Incretin-Based Therapies: What Do We Know So Far?
Pablo F. Mora, Eric L. Johnson
Endocrine Practice.2017; 23(1): 89. CrossRef - Treatment of Dyslipidemias to Prevent Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Maryam Khavandi, Francisco Duarte, Henry N. Ginsberg, Gissette Reyes-Soffer
Current Cardiology Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Sodium butyrate has context-dependent actions on dipeptidyl peptidase-4 and other metabolic parameters
Eun-Sol Lee, Dong-Sung Lee, Prakash Raj Pandeya, Youn-Chul Kim, Dae-Gil Kang, Ho-Sub Lee, Byung-Chul Oh, Dae Ho Lee
The Korean Journal of Physiology & Pharmacology.2017; 21(5): 519. CrossRef - Risk of Myopathy Associated With DPP-4 Inhibitors in Combination With Statins: A Disproportionality Analysis Using Data From the WHO and French Spontaneous Reporting Databases
Vanessa Labat, Mickael Arnaud, Ghada Miremont-Salamé, Francesco Salvo, Bernard Bégaud, Antoine Pariente
Diabetes Care.2017; 40(3): e27. CrossRef - Soluble DPP-4 up-regulates toll-like receptors and augments inflammatory reactions, which are ameliorated by vildagliptin or mannose-6-phosphate
Dong-Sung Lee, Eun-Sol Lee, Md. Morshedul Alam, Jun-Hyeog Jang, Ho-Sub Lee, Hyuncheol Oh, Youn-Chul Kim, Zahid Manzoor, Young-Sang Koh, Dae-Gil Kang, Dae Ho Lee
Metabolism.2016; 65(2): 89. CrossRef - A Multifactorial Approach to Reduce Cardiovascular Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Now More Than Ever
Jan N. Basile
Hospital Practice.2016; 44(1): 9. CrossRef - Association between DPP4 gene polymorphism and serum lipid levels in Chinese type 2 diabetes individuals
Xiaomin Xing, Yi Han, Xiaojun Zhou, Bo Zhang, Yan Li, Zhongsu Wang, Lin Liao, Lequn Su
Neuropeptides.2016; 60: 1. CrossRef - Common medications used by patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: what are their effects on the lipid profile?
Paul D. Rosenblit
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibition and narrow-band ultraviolet-B light in psoriasis (DINUP): study protocol for a randomised controlled trial
Maeve Lynch, Tomás B. Ahern, Irene Timoney, Cheryl Sweeney, Genevieve Kelly, Rosalind Hughes, Anne-Marie Tobin, Donal O’Shea, Brian Kirby
Trials.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of different dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors on metabolic parameters in patients with type 2 diabetes undergoing dialysis
Se Hee Park, Joo Young Nam, Eugene Han, Yong-ho Lee, Byung-Wan Lee, Beom Seok Kim, Bong-Soo Cha, Chul Sik Kim, Eun Seok Kang
Medicine.2016; 95(32): e4543. CrossRef - Incretin-based therapies for obesity treatment
Aline Haas de Mello, Morgana Prá, Larissa Colonetti Cardoso, Rosiane de Bona Schraiber, Gislaine Tezza Rezin
Metabolism.2015; 64(9): 967. CrossRef - Brain signaling systems in the Type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome: promising target to treat and prevent these diseases
Alexander O Shpakov, Kira V Derkach, Lev M Berstein
Future Science OA.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative analysis of therapeutic efficiency and costs (experience in Bulgaria) of oral antidiabetic therapies based on glitazones and gliptins
Elena Pavlova Filipova, Katya Hristova Uzunova, Toni Yonkov Vekov
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Antidiabetic Effect of Galantamine: Novel Effect for a Known Centrally Acting Drug
Mennatallah A. Ali, Hanan S. El-Abhar, Maher A. Kamel, Ahmed S. Attia, John Calvert
PLOS ONE.2015; 10(8): e0134648. CrossRef - The Nonglycemic Actions of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors
Na-Hyung Kim, Taeyang Yu, Dae Ho Lee
BioMed Research International.2014; 2014: 1. CrossRef - A Post Hoc Analysis of HbA1c, Hypoglycemia, and Weight Change Outcomes with Alogliptin vs Glipizide in Older Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Morgan Bron, Craig Wilson, Penny Fleck
Diabetes Therapy.2014; 5(2): 521. CrossRef - Response: The Effect of DPP-4 Inhibitors on Metabolic Parameters in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes (Diabetes Metab J2014;38:211-9)
EunYeong Choe, Eun Seok Kang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2014; 38(4): 319. CrossRef - Letter: The Effect of DPP-4 Inhibitors on Metabolic Parameters in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes (Diabetes Metab J2014;38:211-9)
Seung-Hwan Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2014; 38(4): 317. CrossRef
- Insulin Tregopil: An Ultra-Fast Oral Recombinant Human Insulin Analog: Preclinical and Clinical Development in Diabetes Mellitus
- Serum Adiponectin and Type 2 Diabetes: A 6-Year Follow-Up Cohort Study
- Sun Ha Jee, Chul Woo Ahn, Jong Suk Park, Chang Gyu Park, Hyon-Suk Kim, Sang-Hak Lee, Sungha Park, Myoungsook Lee, Chang Beom Lee, Hye Soon Park, Heejin Kimm, Sung Hee Choi, Jidong Sung, Seungjoon Oh, Hyojee Joung, Sung Rae Kim, Ho-Joong Youn, Sun Mi Kim, Hong Soo Lee, Yejin Mok, Eunmi Choi, Young Duk Yun, Soo-Jin Baek, Jaeseong Jo, Kap Bum Huh
- Diabetes Metab J. 2013;37(4):252-261. Published online August 14, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2013.37.4.252
- 5,106 View
- 40 Download
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Studies on factors which may predict the risk of diabetes are scarce. This prospective cohort study was conducted to determine the association between adiponectin and type 2 diabetes among Korean men and women.
Methods A total of 42,845 participants who visited one of seven health examination centers located in Seoul and Gyeonggi province, Republic of Korea between 2004 and 2008 were included in this study. The incidence rates of diabetes were determined through December 2011. To evaluate the effects of adiponectin on type 2 diabetes, the Cox proportional hazard model was used.
Results Of the 40,005 participants, 959 developed type 2 diabetes during a 6-year follow-up. After the adjustment for age, body mass index (BMI), and waist circumference, the risks for type 2 diabetes in participants with normoglycemia had a 1.70-fold (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.21 to 2.38) increase in men and a 1.83-fold (95% CI, 1.17 to 2.86) increase in women with the lowest tertile of adiponectin when compared to the highest tertile of adiponectin. For participants with impaired fasting glucose (IFG), the risk for type 2 diabetes had a 1.46-fold (95% CI, 1.17 to 1.83) increase in men and a 2.52-fold (95% CI, 1.57 to 4.06) increase in women with the lowest tertile of adiponectin. Except for female participants with normoglycemia, all the risks remained significant after the adjustment for fasting glucose and other confounding variables. Surprisingly, BMI and waist circumference were not predictors of type 2 diabetes in men or women with IFG after adjustment for fasting glucose and other confounders.
Conclusion A strong association between adiponectin and diabetes was observed. The use of adiponectin as a predictor of type 2 diabetes is considered to be useful.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Adiponectin and metabolic cardiovascular diseases: Therapeutic opportunities and challenges
Xiaotian Lei, Sheng Qiu, Gangyi Yang, Qinan Wu
Genes & Diseases.2023; 10(4): 1525. CrossRef - Low levels of total and high-molecular-weight adiponectin may predict non-alcoholic fatty liver in Korean adults
Young-Sang Kim, Soo-Hyun Lee, Seung Geon Park, Bo Youn Won, Hyejin Chun, Doo-Yeoun Cho, Moon-Jong Kim, Ji Eun Lee, Ji-Hee Haam, Kunhee Han
Metabolism.2020; 103: 154026. CrossRef - Anti-inflammatory effects of sucrose-derived oligosaccharides produced by a constitutive mutant L. mesenteroides B-512FMCM dextransucrase in high fat diet-fed mice
Min-Gyung Kang, Hee Jae Lee, Jae-Young Cho, Kanghwa Kim, Soo Jin Yang, Doman Kim
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2016; 477(3): 350. CrossRef - Adiponectin as a Protective Factor Against the Progression Toward Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Postmenopausal Women
Hossein Darabi, Alireza Raeisi, Mohammad Reza Kalantarhormozi, Afshin Ostovar, Majid Assadi, Kamyar Asadipooya, Katayoun Vahdat, Sina Dobaradaran, Iraj Nabipour
Medicine.2015; 94(33): e1347. CrossRef - Effect of ketotifen in obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Sahar M. El-Haggar, Wael F. Farrag, Fedaa A. Kotkata
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2015; 29(3): 427. CrossRef - Smoking and Diabetes: Is the Association Mediated by Adiponectin, Leptin, or C-reactive Protein?
Esayas Haregot Hilawe, Hiroshi Yatsuya, Yuanying Li, Mayu Uemura, Chaochen Wang, Chifa Chiang, Hideaki Toyoshima, Koji Tamakoshi, Yan Zhang, Nobuo Kawazoe, Atsuko Aoyama
Journal of Epidemiology.2015; 25(2): 99. CrossRef - Association between the level of circulating adiponectin and prediabetes: A meta‐analysis
Huasheng Lai, Nie Lin, Zhenzhen Xing, Huanhuan Weng, Hua Zhang
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2015; 6(4): 416. CrossRef - Adiponectin as a Biomarker of Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women: Controversies
Anna Lubkowska, Aleksandra Dobek, Jan Mieszkowski, Wojciech Garczynski, Dariusz Chlubek
Disease Markers.2014; 2014: 1. CrossRef - Modulation of adiponectin as a potential therapeutic strategy
Soo Lim, Michael J. Quon, Kwang Kon Koh
Atherosclerosis.2014; 233(2): 721. CrossRef
- Adiponectin and metabolic cardiovascular diseases: Therapeutic opportunities and challenges
- Diabetes Epidemics in Korea: Reappraise Nationwide Survey of Diabetes "Diabetes in Korea 2007"
- Ie Byung Park, Jaiyong Kim, Dae Jung Kim, Choon Hee Chung, Jee-Young Oh, Seok Won Park, Juneyoung Lee, Kyung Mook Choi, Kyung Wan Min, Jeong Hyun Park, Hyun Shik Son, Chul Woo Ahn, Hwayoung Kim, Sunhee Lee, Im Bong Lee, Injeoung Choi, Sei Hyun Baik
- Diabetes Metab J. 2013;37(4):233-239. Published online August 14, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2013.37.4.233
- 5,336 View
- 59 Download
- 62 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader There are many studies on the prevalence, clinical characteristics, and economic burden of diabetes across the past four decades in Korea. Nonetheless, there is a dearth of nationwide study regarding diabetes encompassing all age group. Eight years ago, the Committee on the Epidemiology of Diabetes Mellitus of Korean Diabetes Association collaborated with Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service to evaluate the status of diabetes care and characteristics in diabetic patients in Korea. In 2007, the collaborative task force team published a comprehensive survey titled "Diabetes in Korea 2007." In this review, we reappraise the diabetic epidemics from the joint report and suggest further studies that are needed to be investigated in the future.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Revisiting the Diabetes Crisis in Korea: Call for Urgent Action
Jun Sung Moon
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(1): 1. CrossRef - Risk assessment and classification for foot ulceration among patients with type 2 diabetes in South Korea
Eun Joo Lee, Ihn Sook Jeong, In Ju Kim, Young Hye Cho, Yun Jin Kim
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Using real-world data for supporting regulatory decision making: Comparison of cardiovascular and safety outcomes of an empagliflozin randomized clinical trial versus real-world data
Ha Young Jang, In-Wha Kim, Jung Mi Oh
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Differences in health behavior and nutrient intake status between diabetes-aware and unaware Korean adults based on the Korea national health and nutrition examination survey 2016–18 data: A cross-sectional study
Anshul Sharma, Chen Lulu, Kee-Ho Song, Hae-Jeung Lee
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Do statins benefit low-risk population for primary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: A retrospective cohort study
In Sun Ryou, Ju Young Kim, Hwa Yeon Park, Sohee Oh, Sehun Kim, Hwa Jung Kim
Frontiers in Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between oseltamivir use and neuropsychiatric adverse events in influenza patients: a nationwide population-based cohort study
Hye-Rim Kang, Suk-Chan Jang, Ju-Young Shin
Expert Opinion on Drug Safety.2021; 20(2): 245. CrossRef - Effectiveness and safety of sodium‐glucose co‐transporter‐2 inhibitors compared with dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitors in older adults with type 2 diabetes: A nationwide population‐based study
Seung Jin Han, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Nami Lee, Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2021; 23(3): 682. CrossRef - Cost-Effectiveness of Tiotropium in Elderly Patients with Severe Asthma Using Real-World Data
Sung-Hyun Hong, Jeong-Yeon Cho, Tae-Bum Kim, Eui-Kyung Lee, Sun-Hong Kwon, Ju-Young Shin
The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice.2021; 9(5): 1939. CrossRef - Dapagliflozin improves cardiovascular risk factors in Emirati patients with T2DM
Aml Mohamed Nada, Mariam Adel Younan
Therapeutic Advances in Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 12: 204201882199536. CrossRef - Association between socioeconomic position and diabetic foot ulcer outcomes: a population-based cohort study in South Korea
Jeong Hyun Ha, Heejin Jin, Ji-Ung Park
BMC Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Etiology, diagnosis, complications, and treatments of diabetic foot
Dong-Kyo Seo
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2021; 64(8): 523. CrossRef - Hospital admissions due to endocrine diseases in Korean male firefighters
Seunghoon Ryu, Yong-Jin Lee, Eun-Chul Jang, Soon-Chan Kwon, KiSeok Kim, Yeon-Soon Ahn, Young-Sun Min
Annals of Occupational and Environmental Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between Frequency of Breakfast Consumption and Insulin Resistance Using Triglyceride-Glucose Index: A Cross-Sectional Study of the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016–2018)
Hye Jin Joo, Gyu Ri Kim, Eun-Cheol Park, Sung-In Jang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(9): 3322. CrossRef - Review of Diabetic Foot Complication Assessment Tools Developed from 2007 to 2016
Yoonhee Lee, Youngshin Song
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2019; 26(4): 231. CrossRef - Associations between Breastfeeding and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Glycemic Control in Parous Women: A Nationwide, Population-Based Study
Ga Eun Nam, Kyungdo Han, Do-Hoon Kim, Youn Huh, Byoungduck Han, Sung Jung Cho, Yong Gyu Park, Yong-Moon Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(2): 236. CrossRef - Risk of osteoporosis in patients with chronic inflammatory neuropathy- a population-based cohort study
Seung Woo Kim, Eun Hwa Kim, Jinae Lee, Young-Chul Choi, Seung Min Kim, Ha Young Shin
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Differences in the risk of mood disorders in patients with asthma-COPD overlap and in patients with COPD alone: a nationwide population-based retrospective cohort study in Korea
Hye-Rim Kang, Sung-Hyun Hong, So-Young Ha, Tae-Bum Kim, Eui-Kyung Lee
Respiratory Research.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - A Comparison of Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists to Low-Dose Inhaled Corticosteroids in the Elderly with Mild Asthma
Sung-Hyun Hong, Hye-Rim Kang, Jin Hyun Nam, Sun-Kyeong Park, Tae-Bum Kim, Eui-Kyung Lee
The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice.2019; 7(8): 2642. CrossRef - The Need to Improve the Quality of Diabetes Care in Korea
Seung Jin Han, Dae Jung Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Fifty Years of Compassionate Care and Harmonious Collaboration of the Korean Diabetes Association: The 50th Anniversary of Korean Diabetes Association
Jong Chul Won, Eun-Jung Rhee, Hyung Joon Yoo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(6): 475. CrossRef - Depth and combined infection is important predictor of lower extremity amputations in hospitalized diabetic foot ulcer patients
Eun-Gyo Jeong, Sung Shim Cho, Sang-Hoon Lee, Kang-Min Lee, Seo-Kyung Woo, Yoongoo Kang, Jae-Seung Yun, Seon-Ah Cha, Yoon-Jung Kim, Yu-Bae Ahn, Seung-Hyun Ko, Jung-Min Lee
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2018; 33(5): 952. CrossRef - Favorable glycemic response after pancreatoduodenectomy in both patients with pancreatic cancer and patients with non-pancreatic cancer
Seo Young Sohn, Eun Kyung Lee, Sung-Sik Han, You Jin Lee, Yul Hwangbo, Young Hwa Kang, Seung Duk Lee, Seong Hoon Kim, Sang Myung Woo, Woo Jin Lee, Eun Kyung Hong, Sang-Jae Park
Medicine.2018; 97(18): e0590. CrossRef - Clinical Importance of Diabetic Neuropathy
Tae Sun Park
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2018; 19(3): 147. CrossRef - Women are less likely than men to achieve optimal glycemic control after 1 year of treatment: A multi-level analysis of a Korean primary care cohort
Seung-Ah Choe, Joo Yeong Kim, Young Sun Ro, Sung-Il Cho, Antonio Palazón-Bru
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(5): e0196719. CrossRef - Diagnosis and Management of Diabetic Foot
Chang Won Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2018; 19(3): 168. CrossRef - HbA1c Cutoff for Prediabetes and Diabetes Based on Oral Glucose Tolerance Test in Obese Children and Adolescents
Hyo-Kyoung Nam, Won Kyoung Cho, Jae Hyun Kim, Young-Jun Rhie, Sochung Chung, Kee-Hyoung Lee, Byung-Kyu Suh
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes Fact Sheet in Korea, 2016: An Appraisal of Current Status
Jong Chul Won, Jae Hyuk Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim, Eun Seok Kang, Kyu Chang Won, Dae Jung Kim, Moon-Kyu Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(5): 415. CrossRef - Risk factors of asthma exacerbation based on asthma severity: a nationwide population-based observational study in South Korea
Hye-Rim Kang, Hyun Jin Song, Jin Hyun Nam, Sung-Hyun Hong, So-Young Yang, SangEun Ju, Sang Won Lee, Tae-Bum Kim, Hye-Lin Kim, Eui-Kyung Lee
BMJ Open.2018; 8(3): e020825. CrossRef - Foot Care for Diabetic Patients
Hye Jung Cha
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2018; 19(1): 41. CrossRef - Risk of new-onset diabetes among patients treated with statins according to hypertension and gender: Results from a nationwide health-screening cohort
Sang-Eun Lee, Ji Min Sung, In-Jeong Cho, Hyeon Chang Kim, Hyuk-Jae Chang, Lamberto Manzoli
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(4): e0195459. CrossRef - Treatment variation related to comorbidity and complications in type 2 diabetes
Yeon Young Cho, Sung-il Cho
Medicine.2018; 97(37): e12435. CrossRef - Efficacy of Body Weight Reduction on the SGLT2 Inhibitor in People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Hyun A Cho, Young Lee Jung, Yong Hoon Lee, Yu Chang Lee, Jung Eun Lee, Sol Jae Lee, Su Jin Jeong, Chong Hwa Kim
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2017; 26(2): 107. CrossRef - Physician-Directed Diabetes Education without a Medication Change and Associated Patient Outcomes
Hun-Sung Kim, Hyunah Kim, Hae-Kyung Yang, Eun Young Lee, Yoo Jin Jeong, Tong Min Kim, So Jung Yang, Seo Yeon Baik, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, In Young Choi, Hyeon Woo Yim, Bong-Yun Cha
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(3): 187. CrossRef - Current status of managing diabetes mellitus in Korea
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2016; 31(5): 845. CrossRef - 7th Asian PAD Workshop
Annals of Vascular Diseases.2016; 9(2): 135. CrossRef - Trends in Diabetes Incidence in the Last Decade Based on Korean National Health Insurance Claims Data
Sun Ok Song, Yong-ho Lee, Dong Wook Kim, Young Duk Song, Joo Young Nam, Kyoung Hye Park, Dae Jung Kim, Seok Won Park, Hyun Chul Lee, Byung-Wan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 31(2): 292. CrossRef - Trends of antidiabetic drug use in adult type 2 diabetes in Korea in 2002–2013
Seung-Hyun Ko, Dae-Jung Kim, Jong-Heon Park, Cheol-Young Park, Chang Hee Jung, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Joong-Yeol Park, Kee-Ho Song, Kyungdo Han, Ki-Up Lee, Kyung-Soo Ko
Medicine.2016; 95(27): e4018. CrossRef - Glycosylated Hemoglobin Threshold for Predicting Diabetes and Prediabetes from the Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Sangmo Hong, Jun Goo Kang, Chul Sik Kim, Seong Jin Lee, Cheol-Young Park, Chang Beom Lee, Sung-Hee Ihm
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2016; 40(2): 167. CrossRef - Predictive Value of Glucose Parameters Obtained From Oral Glucose Tolerance Tests in Identifying Individuals at High Risk for the Development of Diabetes in Korean Population
Hae Kyung Yang, Hee-Sung Ha, Marie Rhee, Jin-Hee Lee, Yong-Moon Park, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Hyeon-Woo Yim, Moo-Il Kang, Won-Chul Lee, Ho-Young Son, Seung-Hwan Lee, Kun-Ho Yoon
Medicine.2016; 95(10): e3053. CrossRef - Serum preadipocyte factor 1 concentrations and risk of developing diabetes: a nested case–control study
S. H. Lee, M. Rhee, H. K. Yang, H. S. Ha, J. H. Lee, H. S. Kwon, Y. M. Park, H. W. Yim, M. I. Kang, W. C. Lee, H. Y. Son, K. H. Yoon
Diabetic Medicine.2016; 33(5): 631. CrossRef - Is an Oral Glucose Tolerance Test Still Valid for Diagnosing Diabetes Mellitus?
Dong-Lim Kim, Sun-Doo Kim, Suk Kyeong Kim, Sooyoun Park, Kee-Ho Song
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2016; 40(2): 118. CrossRef - Fasting plasma glucose concentrations for specified HbA1c goals in Korean populations: data from the Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES V-2, 2011)
Sangmo Hong, Jun Goo Kang, Chul Sik Kim, Seong Jin Lee, Chang Beom Lee, Sung-Hee Ihm
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Combined use of basal insulin analog and acarbose reduces postprandial glucose in patients with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes
Ji‐Hyun Kim, Ji‐Hyun Ahn, Soo‐Kyung Kim, Dae‐Ho Lee, Hye‐Soon Kim, Ho‐Sang Shon, Hyun‐Jeong Jeon, Tae‐Hwa Kim, Yong‐Wook Cho, Jae‐Taek Kim, Sung‐Min Han, Choon‐Hee Chung, Ohk‐Hyun Ryu, Jae‐Min Lee, Soon‐Hee Lee, Min‐Jeong Kwon, Tae‐kyun Kim, Il‐Seong Namg
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2015; 6(2): 219. CrossRef - Anti-Oxidative and Anti-Diabetic Effects of Methanol Extracts from Medicinal Plants
Youn Ri Lee, Nara Yoon
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2015; 44(5): 681. CrossRef - Associations Between the Continuity of Ambulatory Care of Adult Diabetes Patients in Korea and the Incidence of Macrovascular Complications
Young-Hoon Gong, Seok-Jun Yoon, Hyeyoung Seo, Dongwoo Kim
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.2015; 48(4): 188. CrossRef - Statin eligibility and cardiovascular risk burden assessed by coronary artery calcium score: Comparing the two guidelines in a large Korean cohort
Eun-Jung Rhee, Se Eun Park, Hyung Geun Oh, Cheol-Young Park, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Ron Blankstein, Jorge Plutzky, Won-Young Lee
Atherosclerosis.2015; 240(1): 242. CrossRef - Evaluation of low-dose aspirin for primary prevention of ischemic stroke among patients with diabetes: a retrospective cohort study
Ye-Jee Kim, Nam-Kyong Choi, Mi-Sook Kim, Joongyub Lee, Yoosoo Chang, Jong-Mi Seong, Sun-Young Jung, Ju-Young Shin, Ji-Eun Park, Byung-Joo Park
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Health-Related Quality of Life in Coronary Heart Disease in Korea
Hyung Tak Lee, Jinho Shin, Young-Hyo Lim, Kyung Soo Kim, Soon Gil Kim, Jeong Hyun Kim, Heon Kil Lim
Angiology.2015; 66(4): 326. CrossRef - Seroepidemiology of varicella-zoster virus in Korean adolescents and adults using fluorescent antibody to membrane antigen test
S. B. HAN, K. R. KANG, D. H. HUH, H. C. LEE, J. H. KIM, J. H. KANG, S. H. MA
Epidemiology and Infection.2015; 143(8): 1643. CrossRef - Changing Clinical Characteristics according to Insulin Resistance and Insulin Secretion in Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetic Patients in Korea
Jang Won Son, Cheol-Young Park, Sungrae Kim, Han-Kyu Lee, Yil-Seob Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2015; 39(5): 387. CrossRef - Age- and Sex-Specific Relationships between Household Income, Education, and Diabetes Mellitus in Korean Adults: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2008-2010
So-Ra Kim, Kyungdo Han, Jin-Young Choi, Jennifer Ersek, Junxiu Liu, Sun-Jin Jo, Kang-Sook Lee, Hyeon Woo Yim, Won-Chul Lee, Yong Gyu Park, Seung-Hwan Lee, Yong-Moon Park, C. Mary Schooling
PLOS ONE.2015; 10(1): e0117034. CrossRef - Association between Diabetes Education Status and Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: Analysis of the Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES V)
Jun Sung Kwon, Won Jun Kim, Yang Hee Han, Hyun Joong Kim, Sa Young Shin, Kyoo Ho Choi, Jae Hyuck Jun, Myoung Sook Shim, Jin Yeob Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2014; 15(4): 236. CrossRef - The Incidence and Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus and Related Atherosclerotic Complications in Korea: A National Health Insurance Database Study
Bo Kyung Koo, Chang-Hoon Lee, Bo Ram Yang, Seung-sik Hwang, Nam-Kyong Choi, Mohammad Ebrahim Khamseh
PLoS ONE.2014; 9(10): e110650. CrossRef - Current Status of Glycemic Control of Patients with Diabetes in Korea: The Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Ja Young Jeon, Dae Jung Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Soo Lim, Sung Hee Choi, Chul Sik Kim, Jee Hyun An, Nan Hee Kim, Jong Chul Won, Jae Hyeon Kim, Bong-Yun Cha, Kee-Ho Song
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2014; 38(3): 197. CrossRef - Strong correlation between glycaemic variability and total glucose exposure in type 2 diabetes is limited to subjects with satisfactory glycaemic control
S. Suh, J.Y. Joung, S.M. Jin, M.Y. Kim, J.C. Bae, H.D. Park, M.S. Lee, M.K. Lee, J.H. Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism.2014; 40(4): 272. CrossRef - Current Status of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Korea: Report of a Hospital-Based Study of Type 2 Diabetic Patients in Korea by the Diabetic Neuropathy Study Group of the Korean Diabetes Association
Jong Chul Won, Sang Soo Kim, Kyung Soo Ko, Bong-Yun Cha
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2014; 38(1): 25. CrossRef - Impact of Age at First Childbirth on Glucose Tolerance Status in Postmenopausal Women: The 2008–2011 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jin Hwa Kim, Yun Jung, Sang Yong Kim, Hak Yeon Bae
Diabetes Care.2014; 37(3): 671. CrossRef - Predicting the Development of Diabetes Using the Product of Triglycerides and Glucose: The Chungju Metabolic Disease Cohort (CMC) Study
Seung-Hwan Lee, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Yong-Moon Park, Hee-Sung Ha, Seung Hee Jeong, Hae Kyung Yang, Jin-Hee Lee, Hyeon-Woo Yim, Moo-Il Kang, Won-Chul Lee, Ho-Young Son, Kun-Ho Yoon, Maria Eugenia Saez
PLoS ONE.2014; 9(2): e90430. CrossRef - Relationship between socioeconomic status and type 2 diabetes: results from Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) 2010-2012
J. Hwang, C. Shon
BMJ Open.2014; 4(8): e005710. CrossRef - Diabetes Mellitus and Osteoporosis
Kyoung Min Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2013; 14(4): 186. CrossRef - Study on the Correlation between the Nutrient Intakes and Clinical Indices of Type 2 Diabetes Patients
Ji-Young Kwon, Hae-Yun Chung
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2013; 26(4): 909. CrossRef - Role of Sarcopenia in Diabetes Mellitus
Sang Youl Rhee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2013; 14(4): 178. CrossRef
- Revisiting the Diabetes Crisis in Korea: Call for Urgent Action
- Beneficial Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Low Density Lipoprotein Particle Size in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Already under Statin Therapy
- Myung Won Lee, Jeong Kyung Park, Jae Won Hong, Kwang Joon Kim, Dong Yeob Shin, Chul Woo Ahn, Young Duk Song, Hong Keun Cho, Seok Won Park, Eun Jig Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2013;37(3):207-211. Published online June 14, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2013.37.3.207
- 4,163 View
- 46 Download
- 23 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Beyond statin therapy for reducing low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), additional therapeutic strategies are required to achieve more optimal reduction in cardiovascular risk among diabetic patients with dyslipidemia. To evaluate the effects and the safety of combined treatment with omega-3 fatty acids and statin in dyslipidemic patients with type 2 diabetes, we conducted a randomized, open-label study in Korea. Patients with persistent hypertriglyceridemia (≥200 mg/dL) while taking statin for at least 6 weeks were eligible. Fifty-one patients were randomized to receive either omega-3 fatty acid 4, 2 g, or no drug for 8 weeks while continuing statin therapy. After 8 weeks of treatment, the mean percentage change of low density lipoprotein (LDL) particle size and triglyceride (TG) level was greater in patients who were prescribed 4 g of omega-3 fatty acid with statin than in patients receiving statin monotherapy (2.8%±3.1% vs. 2.3%±3.6%,
P =0.024; -41.0%±24.1% vs. -24.2%±31.9%,P =0.049). Coadministration of omega-3 fatty acids with statin increased LDL particle size and decreased TG level in dyslipidemic patients with type 2 diabetes. The therapy was well tolerated without significant adverse effects.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diabetic cardiac autonomic neuropathy: insulin resistance, lipid profile, and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids
Martin-Yurii Markevich, Volodymyr Segin, Victoria Serhiyenko, Alexandr Serhiyenko
InterConf.2023; (35(163)): 213. CrossRef - Atherogenic features of the fatty acid profile of erythrocyte membranes of patients with fatty liver disease of mixed genesis
M. V. Kruchinina, A. V. Belkovets, M. V. Parulikova, A. A. Gromov
Ateroscleroz.2023; 19(4): 350. CrossRef - Omega-3 supplementation in the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) – a review of clinical trials and cohort
Vitoria Melo, Thomas Silva, Thaissa Silva, Juliana Freitas, Joselita Sacramento, Mirian Vazquez, Edilene Araujo
Endocrine Regulations.2022; 56(1): 66. CrossRef - Nutrigenetics, omega-3 and plasma lipids/lipoproteins/apolipoproteins with evidence evaluation using the GRADE approach: a systematic review
Justine Keathley, Véronique Garneau, Valérie Marcil, David M Mutch, Julie Robitaille, Iwona Rudkowska, Gabriela Magdalena Sofian, Sophie Desroches, Marie-Claude Vohl
BMJ Open.2022; 12(2): e054417. CrossRef - N-3 fatty acid supplementation mediates lipid profile, including small dense LDL, when combined with statins: a randomized double blind placebo controlled trial
Gediz Dogay Us, Sohail Mushtaq
Lipids in Health and Disease.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of omega-3 fatty acids and its combination with statins on lipid profile in patients with hypertriglyceridemia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Yunjiao Yang, Wen Deng, Yanmei Wang, Tongyi Li, Yiding Chen, Cong Long, Qing Wen, Yue Wu, Qiu Chen
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Study of the Healthy Effects of Different Fat Ratios Mixtures of Omega-3 to Omega-6 in Male Mice with Alloxan-Induced Diabetes
Ali. M. Atallah, Faryal. F. Hussein
Tikrit journal for agricultural sciences.2021; 21(4): 129. CrossRef - Omega-3 Fatty Acids as Druggable Therapeutics for Neurodegenerative Disorders
Neha M. Chitre, Nader H. Moniri, Kevin S. Murnane
CNS & Neurological Disorders - Drug Targets.2020; 18(10): 735. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Patients Treated with Statins for Residual Hypertriglyceridemia: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial
Ji Eun Jun, In-Kyung Jeong, Jae Myung Yu, Sung Rae Kim, In Kye Lee, Kyung-Ah Han, Sung Hee Choi, Soo-Kyung Kim, Hyeong Kyu Park, Ji-Oh Mok, Yong-ho Lee, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, So Hun Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang, Sang Ah Lee, Chang Beom Lee, Kyung Mook Choi, Sung-Ho Her,
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(1): 78. CrossRef - The combination of canagliflozin and omega-3 fatty acid ameliorates insulin resistance and cardiac biomarkersviamodulation of inflammatory cytokines in type 2 diabetic rats
Mohammed Mohsen Safhi, Tarique Anwer, Gyas Khan, Rahimullah Siddiqui, Sivagurunathan Moni Sivakumar, Mohammad Firoz Alam
The Korean Journal of Physiology & Pharmacology.2018; 22(5): 493. CrossRef - Effect of diets rich in either saturated fat or n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids and supplemented with long-chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on plasma lipoprotein profiles
C B Dias, N Amigo, L G Wood, X Correig, M L Garg
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition.2017; 71(11): 1297. CrossRef - Effects of 12-week supplementation of marine Omega-3 PUFA-based formulation Omega3Q10 in older adults with prehypertension and/or elevated blood cholesterol
Tian Shen, Guoqiang Xing, Jingfen Zhu, Shuxian Zhang, Yong Cai, Donghua Li, Gang Xu, Evan Xing, Jianyu Rao, Rong Shi
Lipids in Health and Disease.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of dietary saturated and n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids on the incorporation of long-chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids into blood lipids
C B Dias, L G Wood, M L Garg
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition.2016; 70(7): 812. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of the efficacy of omega-3 fatty acids for hypertriglyceridaemia management in Korea
H.-S. Kim, H. Kim, Y. J. Jeong, S. J. Yang, S. J. Baik, H. Lee, S.-H. Lee, J. H. Cho, I.-Y. Choi, H. W. Yim, K.-H. Yoon
Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics.2016; 41(5): 508. CrossRef - Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation on Diabetic Nephropathy Progression in Patients with Diabetes and Hypertriglyceridemia
Eugene Han, Yujung Yun, Gyuri Kim, Yong-ho Lee, Hye Jin Wang, Byung-Wan Lee, Bong Soo Cha, Beom Seok Kim, Eun Seok Kang, Wolf-Hagen Schunck
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(5): e0154683. CrossRef - The clinical relevance of omega-3 fatty acids in the management of hypertriglyceridemia
James Backes, Deborah Anzalone, Daniel Hilleman, Julia Catini
Lipids in Health and Disease.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Supercritical fluid extraction of grape seeds: extract chemical composition, antioxidant activity and inhibition of nitrite production in LPS-stimulated Raw 264.7 cells
Concepción Pérez, María Luisa Ruiz del Castillo, Carmen Gil, Gracia Patricia Blanch, Gema Flores
Food & Function.2015; 6(8): 2607. CrossRef - Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids May Attenuate Streptozotocin-Induced Pancreatic β-Cell Death via Autophagy Activation in Fat1 Transgenic Mice
Won-Min Hwang, Dong-Ho Bak, Dong Ho Kim, Ju Young Hong, Seung-Yun Han, Keun-Young Park, Kyu Lim, Dong-Mee Lim, Jae Gu Kang
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(4): 569. CrossRef - Long-chain omega-3 fatty acids, fibrates and niacin as therapeutic options in the treatment of hypertriglyceridemia: A review of the literature
Matthew K. Ito
Atherosclerosis.2015; 242(2): 647. CrossRef - Nutraceuticals and dyslipidaemia: Beyond the common therapeutics
Pietro Scicchitano, Matteo Cameli, Maria Maiello, Pietro Amedeo Modesti, Maria Lorenza Muiesan, Salvatore Novo, Pasquale Palmiero, Pier Sergio Saba, Roberto Pedrinelli, Marco Matteo Ciccone
Journal of Functional Foods.2014; 6: 11. CrossRef - The effect of dietary omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on plasma lipids and lipoproteins of C57BL/6 mice is age and sex specific
K.A. Balogun, R.S. Randunu, S.K. Cheema
Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes and Essential Fatty Acids.2014; 91(1-2): 39. CrossRef - Gene-diet interactions with polymorphisms of the MGLL gene on plasma low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and size following an omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation: a clinical trial
Catherine Ouellette, Iwona Rudkowska, Simone Lemieux, Benoit Lamarche, Patrick Couture, Marie-Claude Vohl
Lipids in Health and Disease.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Saturated fat consumption may not be the main cause of increased blood lipid levels
C.B. Dias, R. Garg, L.G. Wood, M.L. Garg
Medical Hypotheses.2014; 82(2): 187. CrossRef
- Diabetic cardiac autonomic neuropathy: insulin resistance, lipid profile, and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids
- Serum Cystatin C Reflects the Progress of Albuminuria
- Jeong Seon Yoo, Young Mi Lee, Eun Hae Lee, Ji Woon Kim, Shin Young Lee, Ki-Cheon Jeong, Shin Ae Kang, Jong Suk Park, Joo Young Nam, Chul Woo Ahn, Young Duk Song, Kyung Rae Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2011;35(6):602-609. Published online December 26, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.6.602
- 4,515 View
- 38 Download
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Research on the relationship between urinary albumin excretion and serum cystatin C in diabetes is restricted to cross-sectional studies. In this study, we investigated how well serial measurements of serum cystatin C level reflect changes in the urinary albumin excretion rate.
Methods We enrolled and retrospectively collected data on 1,058 participants with type 2 diabetes who were older than 18 years and who had more than 3 years of follow-up with serial measurements of albuminuria and serum cystatin C at an outpatient clinic.
Results With the use of a linear mixed model, we found that the albuminuria level for each patient over time corresponded with the annual change in serum cystatin C-based estimated glomerular filtration rate (cysC-eGFR) but did not correspond with the creatinine-based eGFR calculated by the modification of diet in renal disease formula (MDRD-eGFR). The discrepancy in the direction of the trend was smaller with cysC-eGFR than with MDRD-eGFR.
Conclusion Serum cystatin C level reflects the trend in albuminuria level more accurately than serum creatinine level in Korean type 2 diabetes mellitus patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessment of Cystatin C and Microalbumin as Biomarkers for Nephropathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Bhuneshwar Yadav, Shashidhar K.N, Raveesha A, Muninarayana C.
Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences.2021; 10(25): 1866. CrossRef - Albuminuria Is Associated with Steatosis Burden in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Eugene Han, Mi Kyung Kim, Byoung Kuk Jang, Hye Soon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(5): 698. CrossRef - Increase of BACE1, Brain-Renal Risk Factor, Contributes to Kidney Damage in an Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model
Yan Shi, Feng Gao, Xiaoli Yang, Dongwei Liu, Qiuxia Han, Zhangsuo Liu, Hanyu Zhu, Yong Shen
Journal of Alzheimer's Disease.2020; 76(1): 237. CrossRef - Lower Leg Fat Depots Are Associated with Albuminuria Independently of Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Metabolic Syndrome (Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys 2008 to 2011)
Eugene Han, Nan Hee Cho, Mi Kyung Kim, Hye Soon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(4): 461. CrossRef - Evaluation of creatinine-based and cystatin C-based equations for estimation of glomerular filtration rate in type 1 diabetic patients
Caroline Pereira Domingueti, Rodrigo Bastos Fóscolo, Ana Cristina Simões e Silva, Luci Maria S. Dusse, Janice Sepúlveda Reis, Maria das Graças Carvalho, Ana Paula Fernandes, Karina Braga Gomes
Archives of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 60(2): 108. CrossRef
- Assessment of Cystatin C and Microalbumin as Biomarkers for Nephropathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Low Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Target Goal Attainment Rate in Korean Patients with Diabetes
- Eun Hae Lee, Chul Woo Ahn
- Diabetes Metab J. 2011;35(6):578-579. Published online December 26, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.6.578
- 65,535 View
- 34 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Trends in the management levels of metabolic risk factors in middle-aged and elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: The Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1998–2014
Sukyung Cho, Haeun Jang, Kyong Park, Stefan Kiechl
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(12): e0189361. CrossRef
- Trends in the management levels of metabolic risk factors in middle-aged and elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: The Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1998–2014
- Dietary Oleate Has Beneficial Effects on Every Step of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Progression in a Methionine- and Choline-Deficient Diet-Fed Animal Model
- Ji Young Lee, Jae Hoon Moon, Jong Suk Park, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Chul Woo Ahn, Hyun Chul Lee, Bong Soo Cha
- Diabetes Metab J. 2011;35(5):489-496. Published online October 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.5.489
- 30,189 View
- 34 Download
- 17 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is increasingly recognized as a major cause of liver-related morbidity and mortality. The underlying mechanisms of disease progression remain poorly understood, and primary therapy of NAFLD is not yet established. We investigated the effects of dietary oleate on the development and progression of NAFLD in a methionine- and choline-deficient (MCD) diet-fed animal model.
Methods A total of 30 C57BL/6J mice were randomly divided into three groups (
n =10 in each group) and fed various experimental diets for four weeks: chow, MCD diet, or OMCD (MCD diet with oleate, 0.5 mg/g/day). Liver samples were examined for steatohepatitis and fibrosis parameters and associated genes.Results Additional dietary oleate dramatically reduced MCD diet-induced hepatic steatosis. Hepatic carbohydrate responsive element-binding protein was overexpressed in MCD diet-fed mice, and dietary oleate prevented this overexpression (
P <0.001). Dietary oleate partially prevented MCD diet-induced serum level increases in aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase (P <0.001, respectively). The mRNA expressions of hepatic monocyte chemoattractant protein 1, tumor necrosis factor-α and matrix metalloproteinase-9 were increased in MCD diet-fed mice, and this overexpression of inflammatory molecules was prevented by dietary oleate (P <0.001). Hepatic pericellular fibrosis was observed in MCD diet-fed mice, and dietary oleate prevented this fibrosis. Altogether, dietary oleate prevented MCD diet-induced hepatic steatosis, inflammation and fibrosis.Conclusion Dietary oleate has beneficial effects in every step of NAFLD development and progression and could be a nutritional option for NAFLD prevention and treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bidirectional association between NAFLD and gallstone disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies
Shengying Gu, Shanshan Hu, Shuowen Wang, Chendong Qi, Chenyang Shi, Guorong Fan
Expert Review of Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2023; 17(3): 283. CrossRef - The Effect of Bioactive Aliment Compounds and Micronutrients on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Camelia Munteanu, Betty Schwartz
Antioxidants.2023; 12(4): 903. CrossRef - Single‐cell transcriptomics stratifies organoid models of metabolic dysfunction‐associated steatotic liver disease
Anja Hess, Stefan D Gentile, Amel Ben Saad, Raza‐Ur Rahman, Tim Habboub, Daniel S Pratt, Alan C Mullen
The EMBO Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Histopathological Examination of the Effects of Tocilizumab and Dexamethasone on the Liver in Rats of Oleic Acid induced Acute Lung Injury
Funda TERZİ, Hüseyin Serkan EROL
Balıkesır Health Sciences Journal.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Identifying Lipid Metabolites Influenced by Oleic Acid Administration Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry-Based Lipidomics
Chao Xu, Dan Song, Askild L. Holck, Youyou Zhou, Rong Liu
ACS Omega.2020; 5(20): 11314. CrossRef - Causative and Sanative dynamicity of ChREBP in Hepato-Metabolic disorders
P. Vineeth Daniel, Prosenjit Mondal
European Journal of Cell Biology.2020; 99(8): 151128. CrossRef - PPARδ attenuates hepatic steatosis through autophagy-mediated fatty acid oxidation
Lei Tong, Long Wang, Shuangshuang Yao, Lina Jin, Jian Yang, Yifei Zhang, Guang Ning, Zhiguo Zhang
Cell Death & Disease.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Butyrate Protects Mice Against Methionine–Choline-Deficient Diet-Induced Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis by Improving Gut Barrier Function, Attenuating Inflammation and Reducing Endotoxin Levels
Jianzhong Ye, Longxian Lv, Wenrui Wu, Yating Li, Ding Shi, Daiqiong Fang, Feifei Guo, Huiyong Jiang, Ren Yan, Wanchun Ye, Lanjuan Li
Frontiers in Microbiology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Olive oil combined with Lycium barbarum polysaccharides attenuates liver apoptosis and inflammation induced by carbon tetrachloride in rats
Yun-Yun Chiang, Jane C.-J. Chao
Journal of Functional Foods.2018; 48: 329. CrossRef - Dietary oleic acid regulates hepatic lipogenesis through a liver X receptor-dependent signaling
Simon Ducheix, Alexandra Montagner, Arnaud Polizzi, Frédéric Lasserre, Marion Régnier, Alice Marmugi, Fadila Benhamed, Justine Bertrand-Michel, Laila Mselli-Lakhal, Nicolas Loiseau, Pascal G. Martin, Jean-Marc Lobaccaro, Laurent Ferrier, Catherine Postic,
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(7): e0181393. CrossRef - Is hepatic lipogenesis fundamental for NAFLD/NASH? A focus on the nuclear receptor coactivator PGC-1β
Simon Ducheix, Maria Carmela Vegliante, Gaetano Villani, Nicola Napoli, Carlo Sabbà, Antonio Moschetta
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences.2016; 73(20): 3809. CrossRef - Metformin alleviates hepatosteatosis by restoring SIRT1-mediated autophagy induction via an AMP-activated protein kinase-independent pathway
Young Mi Song, Yong-ho Lee, Ji-Won Kim, Dong-Sik Ham, Eun-Seok Kang, Bong Soo Cha, Hyun Chul Lee, Byung-Wan Lee
Autophagy.2015; 11(1): 46. CrossRef - Adipokines and proinflammatory cytokines, the key mediators in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Sanja Stojsavljević
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2014; 20(48): 18070. CrossRef - Microglial Cell Activation Increases Saturated and Decreases Monounsaturated Fatty Acid Content, but Both Lipid Species are Proinflammatory
Emily B. Button, Andrew S. Mitchell, Marcia M. Domingos, Jessica H.‐J. Chung, Ryan M. Bradley, Ashkan Hashemi, Phillip M. Marvyn, Ashley C. Patterson, Ken D. Stark, Joe Quadrilatero, Robin E. Duncan
Lipids.2014; 49(4): 305. CrossRef - Modeling progressive non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in the laboratory mouse
Jesse D. Riordan, Joseph H. Nadeau
Mammalian Genome.2014; 25(9-10): 473. CrossRef - Rapid chromatographic method to decipher distinct alterations in lipid classes in NAFLD/NASH
Stephan Laggai, Yvette Simon, Theo Ranssweiler, Alexandra K Kiemer, Sonja M Kessler
World Journal of Hepatology.2013; 5(10): 558. CrossRef - Dimethyl sulfoxide reduces hepatocellular lipid accumulation through autophagy induction
Young Mi Song, Sun-Ok Song, Yong-Keun Jung, Eun-Seok Kang, Bong Soo Cha, Hyun Chul Lee, Byung-Wan Lee
Autophagy.2012; 8(7): 1085. CrossRef
- Bidirectional association between NAFLD and gallstone disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies
- Response: Predictive Clinical Parameters for the Therapeutic Efficacy of Sitagliptin in Korean Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J 2011;35:159-65)
- Soon Ae Kim, Woo Ho Shim, Eun Hae Lee, Young Mi Lee, Sun Hee Beom, Eun Sook Kim, Jeong Seon Yoo, Ji Sun Nam, Min Ho Cho, Jong Suk Park, Chul Woo Ahn, Kyung Rae Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2011;35(3):300-301. Published online June 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.3.300
- 3,393 View
- 27 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy and Safety of Switching from Sitagliptin to Ipragliflozin in Obese Japanese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Single-Arm Multicenter Interventional Study
Kentaro Watanabe, Susumu Yamaguchi, Yoshinori Kosakai, Tetsuya Ioji, Hisamitsu Ishihara
Clinical Drug Investigation.2023; 43(12): 927. CrossRef
- Efficacy and Safety of Switching from Sitagliptin to Ipragliflozin in Obese Japanese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Single-Arm Multicenter Interventional Study
- Predictive Clinical Parameters for the Therapeutic Efficacy of Sitagliptin in Korean Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Soon Ae Kim, Woo Ho Shim, Eun Hae Lee, Young Mi Lee, Sun Hee Beom, Eun Sook Kim, Jeong Seon Yoo, Ji Sun Nam, Min Ho Cho, Jong Suk Park, Chul Woo Ahn, Kyung Rae Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2011;35(2):159-165. Published online April 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.2.159
- 4,525 View
- 53 Download
- 40 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Sitagliptin is a highly selective dipeptidyl peptide-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor that increases blood levels of active glucagon-like peptide (GLP)-1 and glucose-dependent insulinotrophic polypeptide (GIP), resulting in increased insulin secretion. While studies conducted in other countries have indicated the efficacy and safety of using sitagliptin to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), its predictors of effects to sitagliptin are not well understood. Therefore, we evaluated the predictive clinical parameters for the therapeutic benefits of sitagliptin when added to an ongoing metformin or sulfonylurea therapy in Korean T2DM subjects.
Methods We obtained data from 251 Korean T2DM subjects who had recently started taking sitagliptin as add-on therapy. Exclusion criteria included any insulin use. Changes in HbA1c (ΔHbA1c) and fasting plasma glucose (ΔFPG) were assessed by comparing baseline levels prior to sitagliptin administration to levels 12 and 24 weeks after treatment. Responders were defined as subjects who experienced decrease from baseline of >10% in ΔHbA1c or >20% in ΔFPG levels at 24 weeks.
Results We classified 81% of the subjects (204 out of 251) as responders. The responder group had a lower mean body mass index (23.70±2.40 vs. 26.00±2.26,
P ≤0.01) and were younger (58.83±11.57 years vs. 62.87±12.09 years,P =0.03) than the non-responder group.Conclusion In Korean T2DM subjects, sitagliptin responders had lower body mass index and were younger compared to non-responders.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Predictors of Responsiveness to GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Insulin-Treated Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Colleen Gavigan, Thomas Donner, Christian S. Goebl
Journal of Diabetes Research.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Comparative Effects of Metformin and Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors in Japanese Obese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Claims Database Study
Masato Odawara, Sumiko Aoi, Tomomi Takeshima, Kosuke Iwasaki
Diabetes Therapy.2021; 12(8): 2165. CrossRef - Reduction in HbA1c with SGLT2 inhibitors vs. DPP-4 inhibitors as add-ons to metformin monotherapy according to baseline HbA1c: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials
A.J. Scheen
Diabetes & Metabolism.2020; 46(3): 186. CrossRef - Factors associated with the glucose‐lowering efficacy of sitagliptin in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Pooled analysis of Japanese clinical trials
Naoko Tajima, Jun‐ichi Eiki, Taro Okamoto, Kotoba Okuyama, Masaru Kawashima, Samuel S Engel
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2020; 11(3): 640. CrossRef - Development of a 13C Stable Isotope Assay for Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Enzyme Activity A New Breath Test for Dipeptidyl Peptidase Activity
Roger Yazbeck, Simone Jaenisch, Michelle Squire, Catherine A. Abbott, Emma Parkinson-Lawrence, Douglas A. Brooks, Ross N. Butler
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Pharmacogenetics of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors in a Taiwanese population with type 2 diabetes
Wen-Ling Liao, Wen-Jane Lee, Ching-Chu Chen, Chieh Hsiang Lu, Chien-Hsiun Chen, Yi-Chun Chou, I-Te Lee, Wayne H-H Sheu, Jer-Yuarn Wu, Chi-Fan Yang, Chung-Hsing Wang, Fuu-Jen Tsai
Oncotarget.2017; 8(11): 18050. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin as add‐on therapy to teneligliptin in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Results of a 24‐week, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial
Takashi Kadowaki, Nobuya Inagaki, Kazuoki Kondo, Kenichi Nishimura, Genki Kaneko, Nobuko Maruyama, Nobuhiro Nakanishi, Hiroaki Iijima, Yumi Watanabe, Maki Gouda
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2017; 19(6): 874. CrossRef - A Practical Review of C-Peptide Testing in Diabetes
Emma Leighton, Christopher AR Sainsbury, Gregory C. Jones
Diabetes Therapy.2017; 8(3): 475. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of linagliptin according to patient baseline characteristics: A pooled analysis of three phase 3 trials
S. Del Prato, S. Patel, S. Crowe, M. von Eynatten
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2016; 26(10): 886. CrossRef - Soluble DPP-4 up-regulates toll-like receptors and augments inflammatory reactions, which are ameliorated by vildagliptin or mannose-6-phosphate
Dong-Sung Lee, Eun-Sol Lee, Md. Morshedul Alam, Jun-Hyeog Jang, Ho-Sub Lee, Hyuncheol Oh, Youn-Chul Kim, Zahid Manzoor, Young-Sang Koh, Dae-Gil Kang, Dae Ho Lee
Metabolism.2016; 65(2): 89. CrossRef - Efficacy of hypoglycemic treatment in type 2 diabetes stratified by age or diagnosed age: a meta-analysis
Xiaoling Cai, Wenjia Yang, Yifei Chen, Xueying Gao, Lingli Zhou, Simin Zhang, Xueyao Han, Linong Ji
Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy.2016; 17(12): 1591. CrossRef - Baseline Body Mass Index and the Efficacy of Hypoglycemic Treatment in Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis
Xiaoling Cai, Wenjia Yang, Xueying Gao, Lingli Zhou, Xueyao Han, Linong Ji, Francesco Giorgino
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(12): e0166625. CrossRef - Predictive Factors for the Therapeutic Response to Concomitant Treatment with DPP-4 Inhibitors in Type 2 Diabetes with Short-Term Follow-Up
Jong-Ha Baek, Bo Ra Kim, Jeong Woo Hong, Soo Kyoung Kim, Jung Hwa Jung, Jaehoon Jung, Jong Ryeal Hahm
Kosin Medical Journal.2016; 31(2): 146. CrossRef - Complementary glucagonostatic and insulinotropic effects of DPP-4 inhibitors in the glucose-lowering action in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes
Ken-ichi Hashimoto, Yukio Horikawa, Jun Takeda
Diabetology International.2016; 7(2): 133. CrossRef - Anagliptin and sitagliptin as add‐ons to metformin for patients with type 2 diabetes: a 24‐week, multicentre, randomized, double‐blind, active‐controlled, phase III clinical trial with a 28‐week extension
S.‐M. Jin, S. W. Park, K.‐H. Yoon, K. W. Min, K.‐H. Song, K. S. Park, J.‐Y. Park, I. B. Park, C. H. Chung, S. H. Baik, S. H. Choi, H. W. Lee, I.‐K. Lee, D.‐M. Kim, M.‐K. Lee
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2015; 17(5): 511. CrossRef - Optimal Candidates for the Switch from Glimepiride to Sitagliptin to Reduce Hypoglycemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Hyun Min Kim, Jung Soo Lim, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun-Seok Kang, Hyun Chul Lee, Bong-Soo Cha
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(1): 84. CrossRef - C-peptide immunoreactivity index is associated with improvement of HbA1c: 2-Year follow-up of sitagliptin use in patients with type 2 diabetes
Takeshi Nishimura, Shu Meguro, Risa Sekioka, Karin Tanaka, Yoshifumi Saisho, Junichiro Irie, Masami Tanaka, Toshihide Kawai, Hiroshi Itoh
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2015; 108(3): 441. CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics and Metabolic Predictors of Rapid Responders to Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor as an Add-on Therapy to Sulfonylurea and Metformin
Ye An Kim, Won Sang Yoo, Eun Shil Hong, Eu Jeong Ku, Kyeong Seon Park, Soo Lim, Young Min Cho, Kyong Soo Park, Hak Chul Jang, Sung Hee Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2015; 39(6): 489. CrossRef - Response to the dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitors in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes might be associated with a diplotype of two single nucleotide polymorphisms on the interleukin‐6 promoter region under a certain level of physical activity
Mizue Matsui, Yoshihiko Takahashi, Noriko Takebe, Kazuma Takahashi, Kan Nagasawa, Hiroyuki Honma, Tomoyasu Oda, Mitsutaka Ono, Riyuki Nakagawa, Takayoshi Sasai, Hirobumi Togashi, Mari Hangai, Takashi Kajiwara, Haruhito Taneichi, Yasushi Ishigaki, Jo Satoh
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2015; 6(2): 173. CrossRef - Effects of Sitagliptin on Insulin and Glucagon Levels in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Ji Hyun Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2015; 39(4): 304. CrossRef - Effects of 6-Month Sitagliptin Treatment on Insulin and Glucagon Responses in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Hae Kyung Yang, Borami Kang, Seung-Hwan Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Kun-Ho Yoon, Bong-Yun Cha, Jae-Hyoung Cho
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2015; 39(4): 335. CrossRef - GLP-1: The Oracle for Gastric Bypass?
Gema Frühbeck, Ruben Nogueiras
Diabetes.2014; 63(2): 399. CrossRef - Effects of concomitant drugs on sitagliptin-mediated improvement in glycemic control in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes
Takumi Hirata, Kouichi Inukai, Jiro Morimoto, Shigehiro Katayama, Hitoshi Ishida
Primary Care Diabetes.2014; 8(3): 265. CrossRef - Predictive clinical parameters for the hemoglobin A1c-lowering effect of vildagliptin in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes
Yukihiro Bando, Masayuki Yamada, Keiko Aoki, Hideo Kanehara, Azusa Hisada, Kazuhiro Okafuji, Daisyu Toya, Nobuyoshi Tanaka
Diabetology International.2014; 5(4): 229. CrossRef - The Effect of DPP-4 Inhibitors on Metabolic Parameters in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Eun Yeong Choe, Yongin Cho, Younjeong Choi, Yujung Yun, Hye Jin Wang, Obin Kwon, Byung-Wan Lee, Chul Woo Ahn, Bong Soo Cha, Hyun Chul Lee, Eun Seok Kang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2014; 38(3): 211. CrossRef - Very Short-Term Effects of the Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor Sitagliptin on the Secretion of Insulin, Glucagon, and Incretin Hormones in Japanese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Analysis of Meal Tolerance Test Data
Kazuki Murai, Tomoyuki Katsuno, Jun-ichiro Miyagawa, Toshihiro Matsuo, Fumihiro Ochi, Masaru Tokuda, Yoshiki Kusunoki, Masayuki Miuchi, Mitsuyoshi Namba
Drugs in R&D.2014; 14(4): 301. CrossRef - Variation at the DPP4 locus influences apolipoprotein B levels in South Asians and exhibits heterogeneity in Europeans related to BMI
Swneke D. Bailey, Changchun Xie, Guillaume Paré, Alexandre Montpetit, Viswanathan Mohan, Salim Yusuf, Hertzel Gerstein, James C. Engert, Sonia S. Anand
Diabetologia.2014; 57(4): 738. CrossRef - Low-dose glimepiride with sitagliptin improves glycemic control without dose-dependency in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on high-dose glimepiride
Rieko Umayahara, Takako Yonemoto, Chika Kyou, Kae Morishita, Tatsuo Ogawa, Yoshitaka Taguchi, Tatsuhide Inoue
Endocrine Journal.2014; 61(12): 1163. CrossRef - The clinical utility of C‐peptide measurement in the care of patients with diabetes
A. G. Jones, A. T. Hattersley
Diabetic Medicine.2013; 30(7): 803. CrossRef - Predictive clinical characteristics for the efficacy of vildagliptin monotherapy in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a multicenter study
Naotsuka Okayama, Kenro Imaeda, Takashi Kato, Soji Iwase, Hideomi Ohguchi, Takashi Joh, Yoshinari Hayashi, Masaya Akao, Kohei Ogawa, Mayo Hachiya, Rei Hattori, Ryosuke Kimura, Sachie Yasui, Misao Ando, Yasunari Jinno, Nobuo Takahashi, Manabu Shimizu, Nobo
Diabetology International.2013; 4(3): 179. CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics of the Responders to Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors in Korean Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes
Tae Jung Oh, Hye Seung Jung, Jae Hyun Bae, Yeong Gi Kim, Kyeong Seon Park, Young Min Cho, Kyong Soo Park, Seong Yeon Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2013; 28(6): 881. CrossRef - Determinants of the HbA1c-lowering effect of sitagliptin when added to ongoing insulin therapy in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes
Yukihiro Bando, Kazuhide Ishikura, Hideo Kanehara, Keiko Aoki, Azusa Hisada, Daisyu Toya, Nobuyoshi Tanaka
Diabetology International.2013; 4(4): 251. CrossRef - The Efficacy of Vildagliptin in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Jun Sung Moon, Kyu Chang Won
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2013; 37(1): 36. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Glycemic Control Response of Sitagliptin
Gun Woo Kim, Jae Hyun Kim, Mi Young Lee, Jang Yel Shin, Young Goo Shin, Eun Ho Ha, Choon Hee Chung
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2013; 14(4): 206. CrossRef - Sitagliptin add-on to low dosage sulphonylureas: efficacy and safety of combination therapy on glycaemic control and insulin secretion capacity in type 2 diabetes
S-I. Harashima, M. Ogura, D. Tanaka, T. Fukushima, Y. Wang, T. Koizumi, M. Aono, Y. Murata, M. Seike, N. Inagaki
International Journal of Clinical Practice.2012; 66(5): 465. CrossRef - Factors predicting therapeutic efficacy of combination treatment with sitagliptin and metformin in type 2 diabetic patients: the COSMETIC study
Soo Lim, Jee Hyun An, Hayley Shin, Ah Reum Khang, Yenna Lee, Hwa Young Ahn, Ji Won Yoon, Seon Mee Kang, Sung Hee Choi, Young Min Cho, Kyong Soo Park, Hak Chul Jang
Clinical Endocrinology.2012; 77(2): 215. CrossRef - Long-term efficacy of sitagliptin for the treatment of type 2 diabetic patients in Japan
Yuji Tajiri, Munehisa Tsuruta, Tsuyoshi Ohki, Tomoko Kato, Yuko Sasaki, Kayo Tanaka, Shusuke Kono, Masayuki Tojikubo, Kentaro Yamada
Endocrine Journal.2012; 59(3): 197. CrossRef - Comparison between sitagliptin as add‐on therapy to insulin and insulin dose‐increase therapy in uncontrolled Korean type 2 diabetes: CSI study
E. S. Hong, A. R. Khang, J. W. Yoon, S. M. Kang, S. H. Choi, K. S. Park, H. C. Jang, H. Shin, G. A. Walford, S. Lim
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2012; 14(9): 795. CrossRef - Letter: Predictive Clinical Parameters for the Therapeutic Efficacy of Sitagliptin in Korean Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J 2011;35:159-65)
Jee-Young Oh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(3): 298. CrossRef - Candidate Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes
Yun-Mi Jang, Dong-Lim Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(2): 117. CrossRef
- Predictors of Responsiveness to GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Insulin-Treated Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- The Association of Brachial-Ankle Pulse Wave Velocity with Acute Postprandial Hyperglycemia in Korean Prediabetic and Diabetic Subjects
- Chul Woo Ahn
- Korean Diabetes J. 2010;34(5):284-286. Published online October 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2010.34.5.284
- 2,321 View
- 26 Download
- 1 Crossref
- Protective Effects of Lithospermic Acid B on Diabetic Nephropathy in OLETF Rats Comparing with Amlodipine and Losartan.
- Eun Seok Kang, Beom Seok Kim, Chul Hoon Kim, Gi Ho Seo, Seung Jin Han, Sung Wan Chun, Kyu Yeon Hur, Chul Woo Ahn, Hunjoo Ha, Mankil Jung, Bong Soo Cha, Hyun Chul Lee
- Korean Diabetes J. 2008;32(1):10-20. Published online February 1, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2008.32.1.10
- 2,390 View
- 19 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Lithospermic acid B (LAB), an active component isolated from Salvia miltiorrhizae, has been reported to have renoprotective effects in type 1 and type 2 diabetic animal models. We examined the effects of LAB on the prevention of diabetic nephropathy compared with amlodipine, a calcium channel blocker, and losartan, an angiotensin receptor blocker, in Otsuka Long-Evans-Tokushima Fatty (OLETF) rats, an animal model of type 2 diabetes. METHODS: LAB (20 mg/kg), amlodipine (10 mg/kg), or losartan (10 mg/kg) was given orally once daily to 10-week-old male OLETF rats for 28 weeks. RESULTS: None of LAB, losartan, and amlodipine exhibited effects on blood glucose levels. Treatment with amlodipine or losartan resulted in similar reductions in blood pressure; however, LAB was less effective in lowering blood pressure. Albuminuria was markedly suppressed by losartan and LAB, but not by amlodipine. LAB treatment decreased levels of renal lipid peroxidation, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), and transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1). CONCLUSION: These results suggest that LAB has beneficial effects on the diabetic nephropathy in OLETF rats by decreasing oxidative stress and inflammation as potent as losartan. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An Overview on Naturally Occurring Phytoconstituent: Lithospermic Acid
Bhupesh Chander Semwal, Amjad Hussain, Sonia Singh
The Natural Products Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- An Overview on Naturally Occurring Phytoconstituent: Lithospermic Acid
- Current Status of Diabetes Management in Korea Using National Health Insurance Database.
- Seok Won Park, Dae Jung Kim, Kyung Wan Min, Sei Hyun Baik, Kyung Mook Choi, Ie Byung Park, Jeong Hyun Park, Hyun Shik Son, Chul Woo Ahn, Jee Young Oh, Juneyoung Lee, Choon Hee Chung, Jaiyong Kim, Hwayoung Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 2007;31(4):362-367. Published online July 1, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/jkda.2007.31.4.362
- 2,837 View
- 33 Download
- 31 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The prevalence of diabetes is steadily increasing in Korea. The increase in number of people with diabetes would ultimately result in premature death, poor quality of life, and increasing economic burden. However, in our country, researches regarding on the quality of diabetes management are lacking. This study was conducted in 2005 using National Health Insurance Database to know the current status of diabetes management in Korea. METHODS: We have randomly selected 3,902 subjects out of 2,503,754 subjects who had claims with diagnosis of diabetes between January 2003 to December 2003 by using two staged cluster sampling method. Field survey with review of medical records and telephone survey was conducted with standardized record forms developed by Korean Diabetes Association; Task Force Team For Basic Statistical Study of Korean Diabetes Mellitus. RESULTS: The age of diabetic subjects was 58.1 +/- 12.6 years and the duration of diabetes was 6.2 +/- 5.5 years. Hypertension was present in 54% of diabetic subjects. Among those with hypertension, 59% were controlled with blood pressure below 140/90 mmHg, but only 19% were controlled with blood pressure below 130/80 mmHg. Hyperlipidemia was present in 29% of diabetic subjects. Only 38% of those with hyperlipidemia were controlled with LDL-cholesterol below 100 mg/dL. For glycemic control, only 40% of diabetic subjects achieved the goal of HbA1c less than 7%, which was suggested by ADA. CONCLUSION: We found that only 20~40% of diabetic subjects in Korea achieved the management goal for glucose, blood pressure, and lipids. It seems urgent to develop a quality management program for diabetes subjects in Korea. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Developing a nomogram for predicting depression in diabetic patients after COVID-19 using machine learning
Haewon Byeon
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Utilization of Diabetes Complication Tests Under the COVID-19 Pandemic: Machine Learning Approach
Haewon Byeon
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Influences of Patient Activation on Diabetes Self-Care Activities and Diabetes-Specific Distress
Sookyung Choi, Su Hyun Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2020; 32(1): 10. CrossRef - Factors Related to Self-care in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Seung-Yeon Kong, Mi-Kyoung Cho
The Open Nursing Journal.2020; 14(1): 64. CrossRef - Current status of treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Ningbo, China
Tianmeng Yang, Rongjiong Zheng, Qingmei Chen, Yushan Mao
Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence and incidence of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and its risk factors in Korea: a nationwide population-based study
Hyungtae Kim, Siin Kim, Sola Han, Pratik P. Rane, Kathleen M. Fox, Yi Qian, Hae Sun Suh
BMC Public Health.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effectiveness of Multidisciplinary Team-Based Education in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes
Jong Ho Kim, Yun Jeong Nam, Won Jin Kim, Kyung Ah Lee, A Ran Baek, Jung Nam Park, Jin Mi Kim, Seo Young Oh, Eun Heui Kim, Min Jin Lee, Yun Kyung Jeon, Bo Hyun Kim, In Joo Kim, Yong Ki Kim, Sang Soo Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2018; 19(2): 119. CrossRef - Physician-Directed Diabetes Education without a Medication Change and Associated Patient Outcomes
Hun-Sung Kim, Hyunah Kim, Hae-Kyung Yang, Eun Young Lee, Yoo Jin Jeong, Tong Min Kim, So Jung Yang, Seo Yeon Baik, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, In Young Choi, Hyeon Woo Yim, Bong-Yun Cha
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(3): 187. CrossRef - Risks of borderline liver enzyme abnormalities to the incidence of impaired fasting glucose and diabetes mellitus: a 7 year follow up study of workers
Jin-Hyun Yu, Jin-Seok Kim, Mee-Ra Lee, Seong-Yong Yoon, Seong-Yong Cho, Seung-Hyun Yoo, Boo-Il Kim
Annals of Occupational and Environmental Medicine.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship Between Duration of Type 2 Diabetes and Self-Reported Participation in Diabetes Education in Korea
Jongnam Hwang, Jeffrey A. Johnson
Asia Pacific Journal of Public Health.2015; 27(2): NP311. CrossRef - Current Status of Management in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus at General Hospitals in South Korea
Jin-Hee Jung, Jung-Hwa Lee, Jin-Won Noh, Jeong-Eun Park, Hee-Sook Kim, Joo-Wha Yoo, Bok-Rye Song, Jeong-rim Lee, Myeong-Hee Hong, Hyang-Mi Jang, Young Na, Hyun-Joo Lee, Jeong-Mi Lee, Yang-Gyo Kang, Sun-Young Kim, Kang-Hee Sim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2015; 39(4): 307. CrossRef - Trend Analysis in the Prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes According to Risk Factors among Korean Adults: Based on the 2001~2009 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data
Young-Ju Kim, Myoung-Nam Lim, Dong-Suk Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2014; 44(6): 743. CrossRef - Evaluating Chronic Care of Public Health Centers in a Metropolitan City
Yong-Jun Choi, Dong-Soo Shin, Minah Kang, Sang-Soo Bae, Jaiyong Kim
Health Policy and Management.2014; 24(4): 312. CrossRef - Increasing risk of diabetes mellitus according to liver function alterations in electronic workers
Kyoungho Lee, Joohee Han, Soo‐Geun Kim
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2014; 5(6): 671. CrossRef - The Effect of the Experience of Diabetes Education on Knowledge, Self-Care Behavior and Glycosylated Hemoglobin in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Seung Hei Moon, Young Whee Lee, Ok-Kyung Ham, Soo-Hyun Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2014; 20(1): 81. CrossRef - Current Status of Prescription in Type 2 Diabetic Patients from General Hospitals in Busan
Ji Hye Suk, Chang Won Lee, Sung Pyo Son, Min Cheol Kim, Jun Hyeob Ahn, Kwang Jae Lee, Ja Young Park, Sun Hye Shin, Min Jeong Kwon, Sang Soo Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Soon Hee Lee, Jeong Hyun Park, In Joo Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2014; 38(3): 230. CrossRef - Effect of Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose Based Diabetes Self-Management Education on Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes
Kang Hee Sim, Moon Sook Hwang
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2013; 19(2): 127. CrossRef - Diabetes Epidemics in Korea: Reappraise Nationwide Survey of Diabetes "Diabetes in Korea 2007"
Ie Byung Park, Jaiyong Kim, Dae Jung Kim, Choon Hee Chung, Jee-Young Oh, Seok Won Park, Juneyoung Lee, Kyung Mook Choi, Kyung Wan Min, Jeong Hyun Park, Hyun Shik Son, Chul Woo Ahn, Hwayoung Kim, Sunhee Lee, Im Bong Lee, Injeoung Choi, Sei Hyun Baik
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2013; 37(4): 233. CrossRef - Total Energy Intake May Be More Associated with Glycemic Control Compared to Each Proportion of Macronutrients in the Korean Diabetic Population
Hye Mi Kang, Dong-Jun Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2012; 36(4): 300. CrossRef - Effect of Soybeans, Chungkukjang, and Doenjang on Blood Glucose and Serum Lipid Profile in Streptozotocin-induced Diabetic Rats
Ah-Ra Kim, Jae-Joon Lee, Sun-Sook Cha, Hae-Choon Chang, Myung-Yul Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2012; 41(5): 621. CrossRef - Comparative Study on Self-Care Behavior, Diabetes-related Stress, and Stress Coping among Good, Inadequate, and Poor Glycemic Control Groups
Hye-Yeon Kang, Mee-Ock Gu
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2012; 19(2): 168. CrossRef - Education as Prescription for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Compliance and Efficacy in Clinical Practice
Mi Yeon Kim, Sunghwan Suh, Sang-Man Jin, Se Won Kim, Ji Cheol Bae, Kyu Yeon Hur, Sung Hye Kim, Mi Yong Rha, Young Yun Cho, Myung-Shik Lee, Moon Kyu Lee, Kwang-Won Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2012; 36(6): 452. CrossRef - Biological Effect of Vaccinium uliginosum L. on STZ-induced Diabetes and Lipid Metabolism in Rats
Eun-Kyung Han, Hyuck-Se Kwon, Se-Gye Shin, Yoon-Hee Choi, Il-Jun Kang, Cha-Kwon Chung
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2012; 41(12): 1727. CrossRef - Comparative Study on HbA1C, Self-care Behavior, and Quality of Life by Depression Status in Type II Diabetic Patients
Young-Min Jeong, Mi-Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2012; 19(3): 353. CrossRef - Therapeutic Target Achievement in Type 2 Diabetic Patients after Hyperglycemia, Hypertension, Dyslipidemia Management
Ah Young Kang, Su Kyung Park, So Young Park, Hye Jeong Lee, Ying Han, Sa Ra Lee, Sung Hwan Suh, Duk Kyu Kim, Mi Kyoung Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(3): 264. CrossRef - Bowl-Based Meal Plan versus Food Exchange-Based Meal Plan for Dietary Intake Control in Korean Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Hee-Jung Ahn, Boo-Kyung Koo, Ji-Yeon Jung, Hwi-Ryun Kwon, Hyun-Jin Kim, Kang-Seo Park, Kyung-Ah Han, Kyung-Wan Min
Korean Diabetes Journal.2009; 33(2): 155. CrossRef - An Evaluation of Sampling Design for Estimating an Epidemiologic Volume of Diabetes and for Assessing Present Status of Its Control in Korea
Ji-Sung Lee, Jaiyong Kim, Sei-Hyun Baik, Ie-Byung Park, Juneyoung Lee
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.2009; 42(2): 135. CrossRef - The Current Status of Type 2 Diabetes Management at a University Hospital
Young Sil Lee
Korean Diabetes Journal.2009; 33(3): 241. CrossRef - The Effect of Gamma-Glutamyltransferase on Impaired Fasting Glucose or Type 2 Diabetes in Korean Men
Tae-Yeon Kim, Do-Hoon Kim, Chang-Hae Park, Kyung-Hwan Cho, Seung-Hwan Lee, Hyuk Ga, Hwan-cheol Kim
Korean Diabetes Journal.2009; 33(3): 215. CrossRef - Management of Diabetic Mellitus in Low-income Rural Patients
Hye-Yeon Kim, Woo-Jun Yun, Min-Ho Shin, Sun-Seong Kweon, Hye-Ran Ahn, Seong-Woo Choi, Young-Hoon Lee, Dong-Hyeok Cho, Jung-Ae Rhee
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.2009; 42(5): 315. CrossRef - The Effect of Smoking Status upon Occurrence of Impaired Fasting Glucose or Type 2 Diabetes in Korean Men
Chang-Hae Park, Hyuk Ga, Jong-Han Leem, Seung-Min Kwak, Hwan-Cheol Kim, Ji-Ho Choi
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.2008; 41(4): 249. CrossRef
- Developing a nomogram for predicting depression in diabetic patients after COVID-19 using machine learning
- In vivo Corneal Confocal Microscopy and Nerve Growth Factor in Diabetic Microvascular Complications.
- Ji Sun Nam, Young Jae Cho, Tae Woong Noh, Chul Sik Kim, Jong Suk Park, Min ho Cho, Hai Jin Kim, Ji Eun Yoon, Han Young Jung, Eun Seok Kang, Yu Mie Rhee, Hyung Keun Lee, Chul Woo Ahn, Bong Soo Cha, Eun Jig Lee, Sung Kil Lim, Kyung Rae Kim, Hyun Chul Lee
- Korean Diabetes J. 2007;31(4):351-361. Published online July 1, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/jkda.2007.31.4.351
- 2,608 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
In vivo corneal confocal microscopy (IVCCM) is being recognized as a non-invasive, early diagnostic tool for diabetic neuropathy, for it provides a clear image of corneal subbasal nerve plexus in detail. Nerve growth factors (NGF) are believed to regulate peripheral and central nervous system, neuronal differentiation, and regeneration of damaged nerves, and their role in diabetic neuropathy is being emphasized these days. Moreover, NGFs and receptors are also expressed in retina and renal mesangial cells, suggesting their possible role in the common pathogenesis of diabetic microvascular complications. We plan to examine corneal structures of diabetic patients and compare IVCCM with conventional tools and analyze their serum and tear NGF levels. METHODS: IVCCM, nerve conduction velocity (NCV), and serum, urine, and tear samplings were done to 42 diabetic patients. From IVCCM, we measured corneal nerve density, branch, and tortuosity, total corneal/epithelial thickness, and the number of endothelial/keratocyte cells, and we checked patients' biochemical profiles and serum and tear NGF levels. RESULTS: Patients with more severe neuropathy had less corneal endothelial cells (3105 +/- 218 vs. 2537 +/- 142 vs. 2350 +/- 73/mm3 vs. 1914 +/- 465/mm3, P = 0.02), higher serum NGF (36 +/- 15 vs. 60 +/- 57.66 vs. 80 +/- 57.63 vs. 109 +/- 60.81 pg/mL, P = 0.39) and tear NGF levels (135.00 +/- 11.94 vs. 304.29 +/- 242.44 vs. 538.50 +/- 251.92 vs. 719.50 +/- 92.63 pg/mL, P = 0.01). There was a positive correlation between neuropathy and corneal nerve tortuosity (r2 = 0.479, P = 0.044) and negative correlation between neuropathy and endothelial cell count (r2 = -0.709, P = 0.002). Interestingly, similar changes were seen in other microvascular complications as well. CONCLUSION: Our results provide a possibility of using novel tools, IVCCM and NGF, as common diagnostic tools for diabetic microvascular complications, but it should be followed by a large population study.

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





